Please enter a keyword to search
In this Code, unless the context otherwise requires, the following definitions will apply.
1.4.1 Accessible Floor Area (AFA)
“Accessible floor area” refers to the total floor area of all covered spaces within a building, including service ducts, lift shafts, toilets, staircases, areas occupied by fixed/ moveable furniture/ equipment/ facilities, and any open-to-sky habitable areas above or below the first storey of the building.
1.4.2 Air well
“Air well” refers to a space(s) enclosed substantially by building(s) and directly open to the sky. An air well can be considered as an external space if it meets the minimum clear width and length below:
| TABLE 1.4.2 - AIR WELL SIZE | |
| Max. Habitable Height of Building | Min. Clear Width and Length of Air Well |
| 18m | 10m |
| 24m | 11m |
| 36m | 12m |
| 48m | 13m |
| 60m and above | 14m |
1.4.3 Ambulatory care facility
"Ambulatory care facility” is a building, or part thereof, used for providing services on an out-patient basis for treatment for patients which would render them incapable of taking action for self-preservation or safety under emergency conditions without assistance from others, such as haemodialysis units or surgical treatment requiring general anaesthesia. Such facilities shall include the followings:
a. Renal dialysis day centres;
b. Aesthetic clinics;
c. Non-mental rehabilitation day centres; and
d. Endoscopy clinics.
1.4.4 Ancillary office
“Ancillary office” refers to any office which supports the activities of a building within Purpose Groups III, V, VI, VII and VIII and which is located within the same building or compartment as the purpose group it serves.
1.4.5 Ancillary usage
“Ancillary usage” refers to a room/ space that serves a supporting function, and which belongs to the same purpose group as the primary building. Such rooms include sick/ first aid rooms, reception lobbies/ areas, waiting areas, staff lounges/ staff recreation rooms, staff changing/ locker rooms, staff training rooms, meeting rooms, workshops, laboratories (no open-flame), store rooms, material/ product holding areas, packing distribution areas within factories/ warehouse buildings, etc.
1.4.6 Anteroom
“Anteroom” refers to the room leading into the BSL-3 or BSL-4 containment laboratory, used for showering and changing. It is also serves as a containment facility for controlling air flow and providing additional physical containment between the laboratory and adjoining spaces.
1.4.7 Approved
“Approved” refers to being approved by the SCDF.
1.4.8 Area of compartment/ room/ space
“Area of compartment/ room/ space” refers to the total area of any compartment/ room/ space bounded by the inner finished surfaces of the walls that form the compartment/ room/ space. Where there is no enclosing wall on any one side, the area of the compartment/ room/ space shall be measured by the outermost edge of the floor on that side.
1.4.9 Area of refuge
“Area of refuge” refers to an area within a building, or in an adjoining building, where evacuees can temporarily take refuge, in lieu of the requirement for adequate exit staircase provision. It shall be adequately separated from the rest of the building or adjoining building by fire-resisting construction, and connected via an external corridor or open-sided linkway. The area of refuge shall be always accessible.
1.4.10 Area of roof
“Area of roof” refers to the visible roof area on a plane parallel to the pitch of the roof.
1.4.11 Area of storey
“Area of storey” refers to the total area of that storey bounded by the inner finished surfaces of the enclosing walls. Where there is no enclosing wall on any one side, the area of storey shall be measured by the outermost edge of the floor on that side.
1.4.12 Assembly occupancy
“Assembly occupancy” refers to buildings or portions of buildings used for gathering of more than 50 persons for such purpose as deliberation, worship, entertainment, eating, drinking, amusement or awaiting transportation.
1.4.13 Atrium
“Atrium” refers to a large open space within a building created by an opening, or a series of openings, in floor assemblies, thus connecting two or more storeys. An atrium is covered at the top and is used for purposes other than those associated with small shafts, e.g., stairs, elevators and various services. The sides of the atrium can be open to all floors, to some floors or closed to all floors by non-rated or rated fire-resistant construction.
1.4.14 Authority having jurisdiction
“Authority having jurisdiction” refers to non-SCDF local entities, which may include an organisation, office, or individual responsible for enforcing the requirement of a code or standard, or for approving equipment, materials, an installation, or a procedure.
1.4.15 Basement storey
“Basement storey” refers to a storey of a building for which at least half the storey height is below the ground level, and which also adjoins its perimeter walls for at least half the length of such walls.
1.4.16 Biological Agent
“Biological Agent” refers to the biological agents stipulated in the First Schedule, Second Schedule and Third Schedule of the Biological Agents and Toxins Act.
1.4.17 Boundary
“Boundary” refers to the border demarcating the area surrounding a building, and where applicable (in determining the relevant boundary), it includes the imaginary extension of the border up to the centre of an abutting street, canal or river.
1.4.18 Capsule hotel
“Capsule hotel” refers to a type of hotel where the bed spaces are enclosed individually. Each bed space is considered as a capsule and not as a loose furniture or fitting. The capsule has the following characteristics:
a. access opening to the bed space can be fitted with doors, curtains or other materials or left open; and
b. the bed space is provided with its individual electricity supply for amenities such as lighting, power points, TV, and other amenities.
1.4.19 Cavity barrier
“Cavity barrier” refers to a fire-rated construction that seals or sub-divides a concealed space. The cavity barrier helps limit the spread of smoke and fire into or within that concealed space.
1.4.20 Ceiling
“Ceiling” refers to a part of a building that encloses and is exposed overhead in a room, circulation space or protected shaft. A soffit or rooflight is regarded as part of its surface, but not the frame of a rooflight.
1.4.21 Circulation space
“Circulation space” refers to the means of access between a room or protected shaft and an exit from the building or compartment. It does not include areas used for any commercial activity, such as information and reception counters, or areas used for exhibitions.
1.4.22 Code of Practice (CoP)
“Code of Practice” refers to the standard of practice acceptable to the authority having jurisdiction. The SCDF may adopt requirements stipulated in the stated year of publication of any referenced Code of Practice, or at its discretion adopt those specified in a later version.
1.4.23 Coldroom
“Coldroom” refers to a room, normally constructed of combustible insulation materials, used for the storage, processing or temporary holding of materials under cold conditions. If the floor area of cold storage space does not exceed 10m2 and its design does not permit persons to walk in, it shall be treated as an appliance and not a coldroom.
1.4.24 Compartment
“Compartment” refers to a part of a building separated from all other parts of the same building by compartment walls and/ or compartment floors. The roof space above the top storey of a compartment is regarded as part of that compartment.
1.4.25 Compartment wall & Compartment floor
“Compartment wall” and “Compartment floor” refer to walls or floors of fire-rated construction provided for the purpose of dividing a building into compartments.
1.4.26 Composite panel
“Composite panel” refers to non-homogenous panel consisting of more than one layer of different materials used for partition, finishes to ceiling/ internal wall/ external walls/ roof covering, etc.
1.4.27 Concealed space/ Cavity
“Concealed space/ Cavity” refers to a space enclosed by elements of a building (including a suspended ceiling or raised floor) or contained within an element. It is not a room, cupboard, circulation space, protected shaft or space within a flue, chute, duct, pipe or conduit.
1.4.28 Corridor
“Corridor” refers to a passage providing means of access from rooms or spaces to an exit.
1.4.29 Cross ventilated corridor/ lobby
“Cross-ventilated corridor/ lobby” refers to a corridor/ lobby with fixed and unobstructed ventilation openings located on opposite facing walls, which face the external space, to allow for air circulation caused by outside breezes or wind.
1.4.30 Cubical extent
“Cubical extent” refers to the volume of a space within a building or compartment. This excludes protected lift walls, exit staircases and other accommodation (such as restrooms and locker rooms) which are enclosed with walls having at least 1-hr fire resistance, and openings protected by doors of ½-hr fire resistance fitted with an automatic self-closing device. It shall be measured according to the following dimensions:
a. the inner finished surfaces of the enclosing walls or, on any side where there is no enclosing wall, a plane extending vertically above the outermost edge of the floor on that side,
b. the upper surface of its lowest floor; and
c. where a building or compartment extends to a roof, the under-surface of the roof or the under-surface of the ceiling of the highest storey within the compartment, including the space occupied by any other wall, or any unprotected shafts, ducts or structure within the space to be so measured.
1.4.31 Custodian care facility
“Custodian-care facility” is a building or part thereof, without stay in accommodation, used by persons who, because of age, or physical or mental disabilities, are unable to care for their self-preservation and safety. Such facilities include the followings:
a. Nurseries for children under 6 years of age (e.g., kindergarten, childcare day centres, infant care day centres, etc.;
b. Senior care day centres;
c. Mentally disabled day care centres;
d. Intellectually disabled day care centres;
e. Mental rehabilitation day care centres; and
f. Psychiatric day care centres.
1.4.32 Dead-end
“Dead-end” refers to a situation within a common area, such as a corridor or lift lobby space, where exit is only possible from one end, with no possible escape from the other end.
1.4.33 Direct distance
“Direct distance” refers to the shortest distance from the most remote point in a room or space, measured within the external enclosures of the room or space to the relevant exits, ignoring internal walls, partitions and fittings other than the enclosure walls of exit passageways and exit staircases.
1.4.34 Door
“Door” refers to any shutter, cover or other form of protection to an opening in any wall, floor or in the structure surrounding a protected shaft, regardless of whether the door is constructed of one or more leaves.
1.4.35 Electromagnetic or electromechanical door-holding device
“Electromagnetic” or “electromechanical door-holding device” refers to a device which holds doors open. This device is designed to automatically close doors in the event of a fire, thereby helping to contain the spread of smoke and fire. Events which cause these devices to trigger include the detection of smoke, failure of power supply to the door, the triggering of a fire alarm, and manual triggering.
1.4.36 Electromagnetic or electromechanical locking device
“Electromagnetic” or “electromechanical locking device” refers to a fail-safe device which provides egress access control. In the event of a fire alarm activation, failure of building power supply, and/ or any fault in the locking devices/ components, related to the release of locking mechanism, this device shall:
a. automatically unlock doors immediately to facilitate egress, and remain so until power supply is restored; and
b. be provided with a means of manual override located within the occupied space, 1.2m above the floor and within 1.5m of the door jamb.
1.4.37 Element of structure
“Element of structure” refers to:
a. a member forming part of the structural frame of a building or any other beam or column but not a member forming part of a roof structure only,
b. a load-bearing wall or load-bearing part of a wall,
c. a floor, including a compartment floor, other than the lowest floor (in contact with the ground) of a building,
d. a separating wall, or
e. a structure enclosing a protected shaft (protecting structure).
1.4.38 Emergency generator
“Emergency generator” refers to emergency power-generating equipment that complies with the requirements stipulated in SS 535.
1.4.39 Emergency lighting
“Emergency lighting” refers to lighting provided with a secondary source of power supply to illuminate the exits and spaces within a building.
1.4.40 Engineered timber
“Engineered timber” refers to mass timber products that are manufactured according to established standards accepted by the SCDF. Examples of mass timber products are Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) and Glued Laminated Timber (GLT) structural elements manufactured in accordance with EN 16351 and EN 14080, respectively.
1.4.41 Evacuee holding area
“Evacuee holding area” refers to a designated circulation area/ space on the refuge floor for temporary assembly of occupants during a fire emergency.
1.4.42 Exit
“Exit” refers to a means of egress from the interior of the building to an external space. An exit includes any of the following, either singly or in combination: a door opening leading to external space, exit staircase, exit ramp and/ or exit passageway, but not including an access stair, aisle, corridor door or corridor and an access door to a room or space.
1.4.43 Exit access
“Exit access” refers to the portion of a means of escape that leads to an exit. It includes the room and building spaces that people occupy, as well as the doors along the escape routes, lobbies, aisles, passageways, corridors, access stairs and ramps traversed in order to reach an exit.
1.4.44 Exit access door
“Exit access door” refers to a door which provides access to a room or space (excluding a toilet cubicle, bedroom, storeroom, utility room, pantry and the like), or installed across the escape path leading to an exit.
1.4.45 Exit door
“Exit door” refers to a door, including a door which opens to the external space, provided at the doorway of an exit for the passage of people, which forms part of the integrity of the exit.
1.4.46 Exit passageway
“Exit passageway” refers to the horizontal extension of a vertical exit via an exit staircase or passage leading from a habitable area to an external space.
1.4.47 Exit staircase
“Exit staircase” refers to a staircase constructed of non-combustible material and protected from fire (by fire-rated construction or located at the external space) for the purpose of enabling egress to the external space.
1.4.48 External corridor
“External corridor” refers to a corridor with an unobstructed and uninterrupted ventilation opening that measures at least 1.2m in vertical height, the latter which is located above its parapet wall.
1.4.49 External exit passageway
“External exit passageway” refers to an exit passageway that serves as required exit with at least one of its longest sides open to the external space or air well.
1.4.50 External exit staircase
“External exit staircase” refers to an exit staircase located outside a building, open to the external space, and that:
a. is enclosed by parapet walls or railing of not more than 1.1m in height;
b. has at least two adjacent sides or one of its longest sides abutting the external space; and
c. is recessed not more than 3m from the building facade.
1.4.51 External space
“External space” refers to an open space abutting the perimeter of a building, which includes an air well and which is vertically open to the sky without any roof or trellis.
1.4.52 External wall (or side of a building)
“External wall” or “external side of a building” refers to an outer wall or vertical enclosure. This includes a part of the roof pitched at an angle of 70º or more to the horizontal, if that part of the roof adjoins a space within the building to which persons have access.
1.4.53 External wall finishes
“External wall finishes” refers to materials/ components installed on the building facade for the purpose of providing thermal insulation, weather resistance and/ or to improve the appearance of buildings. They can be made of timber, metal, brick/stone granite, vinyl, composite materials, etc. It shall include cladding, fins and any decorative features mounted on the external walls of a building.
1.4.54 Fire lift lobby
“Fire lift lobby” refers to a protected and ventilated lobby into which a fire lift opens, and from which direct access to an exit staircase can be made for the purpose of firefighting.
1.4.55 Fire resistance
“Fire resistance” refers to the minimum period of time during which an element of structure or building element can be expected to function satisfactorily while subjected to a standard fire test.
1.4.56 Fire safety report
“Fire safety report” refers to a document that details the provision of fire protection systems, life safety features and fire safety management for a building, plant or installation.
1.4.57 Fire stop
“Fire stop” refers to a seal provided to close an imperfection of fit or any joint between elements, components or construction in a building, which serves to prevent/ limit the passage of smoke and flame through that imperfection or joint.
1.4.58 Flammable refrigerant
“Flammable refrigerant” refers to the group of refrigerants with flammability classification of group 2 or 3 in accordance to ISO 5149. For refrigerant blends which have more than one flammability classification, the most unfavourable classification shall be taken for the purpose of this definition. Most of these flammable refrigerants are hydrocarbon (HC) based. Some examples of HC refrigerant include propane, butane and isobutane.
1.4.59 Flexible joints and Flexible connections
For air-conditioning and mechanical ventilation systems:
a. “flexible joints” refer to connections between ducts and equipment normally provided to isolate vibration and to allow thermal movement; and
b. “flexible connections” refer to flexible sections of ducts provided to connect the extremity of ventilation ductwork to terminal units, extract units and grilles.
1.4.60 Fire engine access road
“Fire engine access road” refers to a road designed for firefighting appliances gain access to, and travel within a development for firefighting operations.
1.4.61 Fire engine accessway
“Fire engine accessway” refers to a metalled or paved road located along the perimeter of a building to allow a firefighting appliance to carry out firefighting operations. Compared to a fire engine access road, a fire engine accessway is designed to withstand a higher tonnage, and with a larger width, for the purpose of deploying firefighting appliances during an operation.
1.4.62 Fully Automated Mechanised Car Park (FAMCP)
“Fully automated mechanised car park” refers to a building or part of a building that is intended for the storage/ parking of passenger vehicles employing fully automated mechanical facilities to move the vehicle from the point of entry to the parking deck and vice-visa. The parking area would be accessible by trained staff when carrying out maintenance works only. The automatic parking system is to be deactivated during the maintenance operations.
1.4.63 General warehouse
“General warehouse” refers to a building or space used for storing various types of goods or materials. It includes warehouses for storing chemicals, fresh/ perishable food products (coldroom), etc. Store having floor area more than 100m2 shall be classified as warehouse.
1.4.64 Habitable floor
“Habitable floor” refers to all floors in a building, including the roof level. The roof level can be taken as non-habitable if it is not used for any purpose/ activity other than housing M&E plants/ equipment, e.g. lift motors, fire pumps, generators, fire hose reel pumps, water supply pumps, water tanks, cooling towers, solar photovoltaic panels, supply/ exhaust fans with associated ductwork, air-con condensing units, telecommunication equipment, satellite dishes, public warning sirens, green roofs inaccessible to public and for maintenance access only, etc
1.4.65 Habitable height
“Habitable height” refers to the height measured from the level of fire engine accessways or fire engine access roads, whichever is the lowest, to the finished floor level of the highest habitable floor.
1.4.66 Height of building
“Height of building” refers to the vertical distance measured from the average level of the ground adjoining the outside of the external walls of the building to the level of half the vertical height of the roof of the building or part, or the top of the walls or of the parapet (if any), whichever is higher.
1.4.67 High containment facility
“High containment facility” refers to containment laboratory, including the interstitial space, waste treatment area, anteroom, etc.) of Bio-safety Level 3 [BSL-3] and maximum containment laboratory of Bio-safety Level 4 [BSL-4] as defined in the WHO Laboratory Bio-Safety Manual. They are designed to comply with the requirements of WHO and authorities having jurisdiction for storing or handling of biological agents.
1.4.68 High hazard occupancy
“High hazard occupancy” refers to any occupancy in which the contents or activities include one or more of the following:
a. materials with auto-ignition temperature lower than 200ºC, or
b. materials that produce poisonous, noxious fumes, or flammable vapour, or
c. materials that cause explosions, or
d. high hazard occupancies stipulated under SS CP 52, or
e. highly combustible substances and/ or flammable liquids.
1.4.69 Hospital
“Hospital” is a building used for medical and surgical care and shall include healthcare facilities with 24-hr or inpatient services, such buildings include the following:
a. General hospitals;
b. Psychiatric hospitals (Institute of Mental Health)
c. Children/ Women hospitals; and
d. Community hospitals.
1.4.70 Load-bearing wall
“Load-bearing wall” refers to a wall which supports any load in addition to its own weight.
1.4.71 Masonry
“Masonry” refers to brick or concrete construction.
1.4.72 Mechanical ventilation
“Mechanical ventilation” refers to any system that uses mechanical means such as ventilation fan, to introduce outdoor air to a space when natural ventilation mode cannot be achieved during normal and fire emergency situations. This includes supply ventilation, exhaust ventilation, pressurisation, smoke purging, mechanical engineered smoke control systems, balanced systems that consist of both supply and exhaust ventilations, etc.
1.4.73 Non-combustible material
“Non-combustible material” refers to any material which neither burns nor gives off flammable vapour in sufficient quantity to ignite when subjected to the test for combustibility prescribed in BS 476 Part 4, and includes materials of limited combustibility, such as:
a. any material of density 300kg/m3 or more, which when tested in accordance with BS 476: Part 11, does not flame, and the rise in temperature on the furnace thermocouple is not more than 20°C;
b. any material with a non-combustible core at least 8mm thick having combustible facings (on one or both sides) not more than 0.5mm thick; and
c. any material of density less than 300kg/m3, which when tested in accordance with BS 476: Part 11,
(1) does not flame for more than 10 sec;
(2) the rise in temperature on the centre (specimen) thermocouple is not more than 35°C; and
(3) the rise in temperature on the furnace thermocouple is not more than 25°C.
1.4.74 Non-load-bearing wall
“Non-load-bearing wall” refers to a wall which supports no load other than its own weight.
1.4.75 Notional boundary
“Notional boundary” refers to an imaginary boundary which exists at equal distance between buildings on the same site, or the centre of the width of a public road/ drain/ sewer reserve, provided that the boundary is fronting the respective reserves.
1.4.76 Nursing care facility
"Nursing care facility" refers to a building, or part thereof, used for the housing and nursing care of persons on a 24-hr basis who, because of physical incapacity, may be unable to care for their own needs and safety without assistance of other persons. These facilities provide inpatient medical care and include the followings:
a. Nursing homes;
b. Convalescent homes; and
c. Hospice.
1.4.77 Occupant load
“Occupant load” of a building, or part thereof, refers to the total number of persons that can occupy such a building, or part thereof, at any one time. The “occupant load” shall be determined by:
a. multiplying the floor area(s) available for occupation with the appropriate areas per person as stated in Table 1.4B, unless prior approval is obtained from SCDF for any other occupancy load factors not stated in this table, or
b. the number of fixed seating, if applicable, for assembly occupancies.
1.4.78 One-way travel
“One-way travel” refers to a situation where occupants within a space can only travel in a single route/ direction, from the most remote point, to an exit or a splitting point to reach multiple exits.
1.4.79 Outdoor Display Area (ODA)
“Outdoor display area” refers to an area along the common walkways in front of their shops where the shop owner/ operator displays his merchandises. The area can be open- to-sky, covered or roofed-over with extended awning/ canopy.
1.4.80 Outdoor Refreshment Area (ORA)
“Outdoor refreshment area” refers to an area along the common walkways in front of their eating houses, restaurants, coffee shops, hawker centres, fast food outlets, cafeterias, canteens, pubs, bars and the like by their respective food & beverage outlet’s owner/ operator. The area can be open-to-sky, covered or roofed-over with umbrella or extended awning/ canopy.
1.4.81 Permitted limit of unprotected area
“Permitted limit of unprotected area” refers to the maximum aggregate area of unprotected areas in any side or external wall of a building or compartment
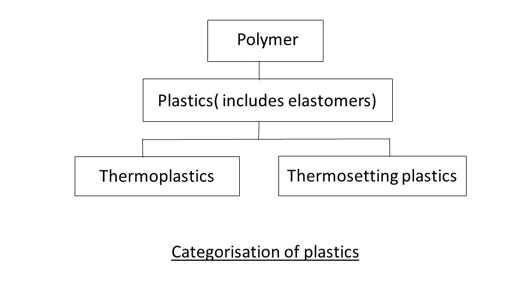
1.4.82 Plastic
“Plastic” refers to any group of organic materials which, though stable in use at ambient temperatures, are plastic at some stage in their manufacture and then can be shaped by the application of heat and/ or pressure. Plastics can be categorised as either thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics.
1.4.83 Pressurisation
“Pressurisation” refers to a mechanical ventilation system that introduce positive differential pressure to a space/ room to prevent smoke ingress during a fire emergency.
1.4.84 Private lift
“Private lift” refers to a passenger lift which is meant for the exclusive use of occupants in the building, and is located to open its door directly into private enclosed spaces. Vehicle lifts, home lifts and stair lifts are not considered private lifts.
1.4.85 Protected shaft
“Protected shaft” refers to an exit staircase, exit passageway, lift, chute, duct or other shaft which enables persons, things or air to pass from one compartment to another.
1.4.86 Protecting structure
“Protecting structure” refers to a wall, floor or other part of the building which encloses a protected shaft. The following are not considered protecting structure:
a. a wall which also forms part of an external wall, separating wall or compartment wall, or
b. a floor which is also a compartment floor or a floor laid directly on the ground, or
c. a roof.
1.4.87 Purpose Group (PG)
1.4.88 Refuge floor
“Refuge floor” refers to a floor adequately separated from the rest of the building by fire-resisting construction. It serves as an area where evacuees can temporarily take refuge for buildings with long vertical evacuation routes to the building’s external space.
1.4.89 Relevant boundary
“Relevant boundary” refers to the lot boundary in relation to a building’s external wall or compartment. For the purpose of unprotected openings setback calculation, it may also be the notional boundary.
1.4.90 Remoteness of exits
“Remoteness of exits” refers to exits which are remotely located from each other, arranged and constructed to minimise the possibility that more than one would be rendered unusable during a fire, or other emergency conditions.
1.4.91 Roof light
“Roof light” refers to any elements in a roof intended to admit daylight.
1.4.92 Room
“Room” refers to an enclosed space bounded by walls that is not an enclosed circulation space or protected shaft at most 750mm in depth.
1.4.93 Separated part (of a building)
“Separated part” refers to a form of compartmentation from another part of the same building by a compartment wall which runs full height of the part and is in one continuous plane.
1.4.94 Separating wall
“Separating wall” refers to a wall used to divide or portion adjoining buildings under different ownership.
1.4.95 Setback distance
“Setback distance” refers to the distance between a building and its relevant boundary, which is meant for the purpose of preventing fire spread between buildings/ properties.
1.4.96 Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF)
“Singapore Civil Defence Force” refers to the Commissioner of Singapore Civil Defence Force and includes officers authorised by him generally or specifically to exercise the powers, functions and duties conferred by the Fire Safety Act.
1.4.97 Single point emergency lighting
“Single point emergency lighting” refers to an emergency lighting system employing self-contained emergency luminaires
1.4.98 Smoke-check door
“Smoke-check door” refers to a door or set of doors placed in an internal corridor to restrict the spread of smoke by reducing draft.
1.4.99 Smoke-free lobby
“Smoke-free lobby” refers to a lobby located at the entrance of an exit staircase. It is designed to help prevent or minimise the entry of smoke into the staircase.
1.4.100 Storey
“Storey” refers to any floor or part thereof, including platforms, mezzanines, attic levels and M&E floors.
1.4.101 Super high-rise residential building
“Super high-rise residential building” refers to a residential building with more than 40 storeys/ levels.
1.4.102 Supervisory care facility
“Supervisory care facility” refers to a building or part thereof, used for the housing, on a 24-hr basis, of mental health patients, natal cares, aged and individuals under welfare cares, who may be capable of self-preservation but require supervision and are receiving therapy, training or other health-related care and for whom there may be security measures not under their control. Such facilities shall include the followings:
a. Homes for intellectually disabled;
b. Psychiatric rehabilitation homes;
c. Dementia homes;
d. Pre/ post natal care centres; and
e. Welfare homes.
1.4.103 Tenancy unit
“Tenancy unit” refers to an individual unit or subdivided unit within a building or a compartment, and which is managed by a different operator registered with the authority having jurisdiction.
1.4.104 Thermoplastics
“Thermoplastic” refers to a class of plastic materials that is capable of being repeatedly softened by heating and hardened by cooling. A material can be considered as thermoplastic if it is a synthetic polymeric material which has a softening point below 200°C when tested to BS EN ISO 306 Method A120 Plastics– Thermoplastic materials – Determination of Vicat softening temperature.
1.4.105 Thermosetting plastic
“Thermosetting plastic” refers to a class of plastic materials that will undergo a chemical reaction by the application of heat, pressure, catalysts, etc., leading to a relatively infusible, non-reversible state.
1.4.106 Toxin
“Toxin” refers to the toxins stipulated in the Fifth Schedule of the Biological Agents and Toxins Act.
1.4.107 Travel distance
“Travel distance” refers to the distance required to be traversed from the most remote point in any room or space to the edge of a door opening, directly to:
a. an exit staircase, or
b. an exit passageway, or
c. an open external space,
unless otherwise permitted under this Code as in the case of residential apartments, maisonettes and exits to areas of refuge.
1.4.108 Two-way travel
“Two-way travel” refers to a situation where occupants within a space have the choice of more than one route/direction from a splitting point to reach multiple exits.
1.4.109 Unmanned building
An “unmanned building” refers to a building which is not manned by operation or security personnel after office or operating hours.
1.4.110 Unprotected area
“Unprotected area”, in relation to a side or external wall of a building, refers to:
a. a window, door or other opening;
b. any part of the external wall which has less than the relevant fire resistance; and
c. any part of the external wall which has combustible material more than 1mm thick attached or applied to its external face, whether for finishes or any other purpose.
1.4.111 Ventilation openings
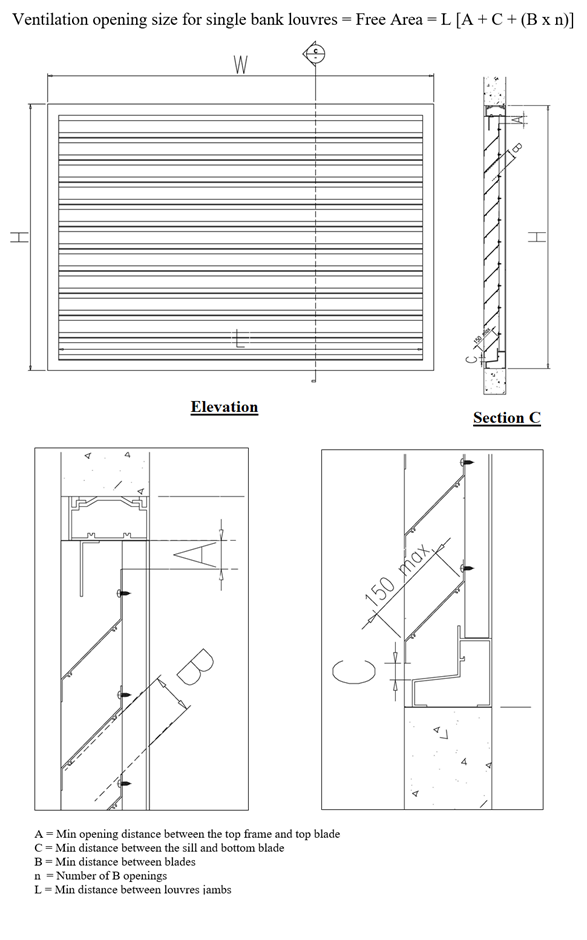
“Ventilation openings” refer to fixed natural ventilation openings located in external walls for any space, which shall be unobstructed at all times, and exclude windows or louvres that are openable or operable. The fixed louvres shall consist of a single bank of louvres with blade width not exceeding 150mm, with effective ventilation openings calculated based on the free area calculation stated below:
1.4.112 Vertical exit
“Vertical exit” refers to an exit staircase or exit ramp which serves as a required exit from one or more storeys above or below ground level.
1.4.113 Wall surface
“Wall surface”, in the context of internal surfaces, refers to the surface of glazing, and any part of the ceiling sloping at an angle of 70º or more to the horizontal. It does not include:
a. door frames and unglazed parts of doors, or
b. window frames and frames in which glazing is fitted, or
c. architraves, cover moulds, picture rails, skirtings and similar narrow members, or
d. fitted furniture.
1.4.114 Workers’ dormitories
“Workers’ dormitories” refers to buildings or spaces in buildings where group sleeping accommodation is provided for workers.
TABLE 1.2A : CODES & STANDARDS
| TABLE 1.2A : CODES & STANDARDS | ||
| Name | Description | Remarks |
| SINGAPORE STANDARDS | ||
SS CP 52 | CoP for Automatic Fire Sprinkler System | |
SS 99 | Specifications for Welded Low Carbon Steel Cylinders for Storage and Transportation of Low-Pressure Liquefiable Gases | |
| SS141 | Specification for Unplasticised PVC pipe for Cold Water Services and Industrial Uses | |
| SS 213 | Unplasticised PVC Pipes and Fittings for Soil, Waste and Vent Application | |
SS 232 Pt 1 to 6 | Portable Fire Extinguishers | Replaced by SS EN 3 - 7 to 10 |
SS 233 | Specifications for Flexible Rubber Tubing, Rubber Hose and Rubber Hose Assemblies for Use in LPG Vapour Phase Installations | |
SS 254 | Electrical Apparatus for Explosive Gas Atmospheres | Replaced by IEC 60079 |
SS 263
Pt 2 | Luminaires - Particular Requirements for Luminaires for Emergency Lighting | Replaced by IEC 60598-2-22 |
SS 281 | Specifications for Pressure Regulators for LPG | |
SS 286 | Caution Labelling for Hazardous Substances | Replaced by SS 586 |
SS 294 | Specifications for Valves for Use with Domestic and Industrial LPG Cylinders | |
SS 299 | Fire Resistant Cables | |
SS 332 | Specification for Fire Door | |
SS 333 | Specification for Fire Dampers | |
SS 489 | Specification for Fire Shutters | |
SS 508 | Graphical Symbols - Safety Colours & Safety Signs | Formerly SS 217 & SS 364 |
| Pt 1 | Design Principles for Safety Signs & Safety Markings | |
| Pt 2 | Design Principles for Product Safety Labels | |
| SS 512 | CoP for the design, construction and operation of pipeline service corridors | |
SS 532 | CoP for the Storage of Flammable Liquids | Formerly CP 40
|
SS 535 | CoP for Installation, Operation, Maintenance, Performance Constructional Requirements of Mains Failure Standby Generating Systems | Formerly CP 31 |
SS 546 | CoP for Emergency Voice Communication Systems in Buildings | Formerly CP 25 |
SS 550 | CoP for Installation, Operation and Maintenance of El Passenger and Goods Lifts | Formerly CP 2 |
SS 551 | CoP for Earthing | Formerly CP 16
|
SS 563 | CoP for the Design, Installation & Maintenance of Em Lighting and Power Supply Systems in Building | Formerly CP 19 |
Pt 1 | Emergency lighting | |
Pt 2 | Installation Requirements and Maintenance Procedures | |
SS 572 | CoP for the Use of Timber in Buildings | Formerly CP 1 |
SS 575 | CoP for Fire Hydrant, Rising Mains and Hose Reel System | Formerly CP 29 |
SS 578 | CoP for the Use and Maintenance of Portable Fire Extinguishers | Formerly CP 55 |
SS 586 | Specification for Hazard Communication for Hazardous Chemicals and Dangerous Goods | Replaces SS 286 |
SS 608 | CoP for Gas Installation | Formerly CP 51 |
| SS 634 | CoP for Fire Safety for Open Plant Processing Facilities in Oil, Chemical and Process Industries | |
| SS 638 | CoP for Electrical Installations | Formerly CP 5 |
| SS 641 | CoP for Fire Safety for Laboratories Using Chemicals | |
| SS 645 | CoP for the Installation and Servicing of Electrical Fire Alarm Systems | Formerly CP 10 |
| SS EN 3-7 | Portable Fire Extinguishers - | Replaces SS 232 Pt 1 to 6 |
| Part 7: Characteristics, performance requirements and test methods | ||
| SS EN 3-8 | Portable Fire Extinguishers - | |
| Part 8: Additional requirements to SS EN 3-7 for the construction, resistance to pressure and mechanical tests for extinguishers with a maximum allowable pressure equal to or lower than 30 bar | ||
| SS EN 3-9 | Portable Fire Extinguishers - | |
| Part 9: Additional requirements to SS EN 3-7 for pressure resistance if CO extinguishers | ||
| SS EN 3-10 | Portable Fire Extinguishers - | |
| Part 10: Provisions for evaluating the conformity of a portable fire extinguisher to SS EN 3-7 | ||
| SS EN 1992 | Design of Concrete Structures | Formerly CP 65 |
| Pt 1 | Planning and Performance Assessment of Electrical Energy Storage Systems – General Specification | |
| Pt 2 | Safety Considerations for Grid- Integrated EES Systems – General Specifications | |
| TR 77 | Electrical Energy Storage (EES) Systems | |
| Pt 1 | Planning and Performance Assessment of Electrical Energy Storage Systems – General Specification | |
| Pt 2 | Safety Considerations for Grid-integrated EES Systems – General Specification | |
| AMERICAN STANDARDS | ||
| ANSI | American National Standard Institute | |
| A14.3 | American National Standards for Ladders - Fixed - Safety Requirements | |
ASTM D635 | Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and/ or Extent & Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position | |
ASTM E108 | Standard Test Methods for Fire Tests of Roof Coverings | |
| ASTM E119 | Standard Test Methods for Fire Tests of Building Construction & Materials | |
| ASTM E 662 | Standard Test Method for Specific Optical Density of Smoke Generated by Solid Materials | |
| ASTM E814 | Standard Test Method for Fire Tests of Penetration Firestop Systems | |
| ASTM E2307 | Standard Test Method for Determining Fire Resistance of Perimeter Fire Barriers Using Intermediate – Scale, Multi-story Test Apparatus | |
| NFPA 16 | Standard for the Installation of Foam-Water Sprinkler and Foam-Water Spray Systems | Formerly NFPA 16A |
| NFPA 30 | Flammable & Combustible Liquids Code | |
| NFPA 33 | Standard for Spray Application Using Flammable or Combustible Materials | |
| NFPA 45 | Standard on Fire Protection for Laboratories Using Chemicals | |
| NFPA 54 | National Fuel Gas Code | |
| NFPA 55 | Compressed Gases and Cryogenic Fluids Code | |
| NFPA 58 | Liquefied Petroleum Gas Code | |
| NFPA 251 | Standard Methods of Tests of Fire Resistance of Building Construction & Materials | |
| NFPA 253 | Standard Method of Test for Critical Radiant Flux of Floor Covering Systems Using a Radiant heat Energy Source | |
| NFPA 258 | Recommended Practice for Determining Smoke Generation of Solid Material | |
| NFPA 262 | Standard Methods of Tests for Flame Travel and Smoke of Wires and Cables for Use in Air-Handling Spaces | |
| NFPA 285 | Standard Fire Test Method for Evaluation of Fire Propagation Characteristics of Exterior Wall Assemblies Containing Combustible Components | |
| NFPA 400 | Hazardous Materials Code | |
| NFPA 430 | Code for the Storage of Liquids & Solid Oxidizers | Replaced by NFPA 400 |
| NFPA 432 | Code for the Storage of Organic Peroxide Formulations | |
| NFPA 495 | Explosive Materials Code | |
| NFPA 502 | Standard for Road Tunnels, Bridges and other Limited Access Highways | |
| NFPA 750 | Standard on Water Mist Fire Protection Systems | |
| NFPA 2001 | Standard on Clean Agent Fire Protection Systems | |
UL 132 | Standard for Safety Relief Valves for Anhydrous Ammonia and LP-Gas | |
UL 144 | Standard for LP-Gas Regulators | |
| UL 217 | Standard for Smoke Alarms | |
| UL 300 | Standard for Fire Testing of Fire Extinguishing Systems for Protection of Commercial Cooking Equipment | |
| UL 448 | Standard for Safety Centrifugal Stationary Pumps for Fire Protection Service | |
| UL 555 | Fire Dampers | |
| UL 924 | Standard for Emergency Lighting and Power Equipment | |
| AUSTRALIAN STANDARDS | ||
| AS 1530 | Methods for Fire Tests on Building Materials, Components & Structures | |
Pt 4 | Fire-resistance Test of Elements of Construction | |
| AS 2208 | Safety Glazing Materials in Buildings | |
| AS/NZS 2293 | Emergency Lighting and Exit Signs for Buildings | |
| Pt 1 | System Design, Installation and Operation | |
| AS 2714 | The Storage & Handling of Organic Peroxides | |
| AS 2941 | Fixed Fire Protection Installations - Pumpset Systems | |
| AS 3786 | Smoke Alarms Using Scattered Light, Transmitted Light or Ionization | |
| AS 4391 | Smoke Management Systems - Hot Smoke Test | |
| AS 4326 | The Storage & Handling of Oxidizng Agents | |
| AS 4587 | Water Mist Fire Protection Systems - System Design, Installation and Commissioning | |
| BRITISH STANDARDS | ||
| BR 186 | Design Principles for Smoke Ventilation in Enclosed Shopping Centres | Published by Fire Research Station, Building Research Establishment, Borehamwood, Herts WD62BL |
| BR 258 | Design Approaches for Smoke Control in Atrium Buildings | |
| BR 368 | Design Methodologies for Smoke and Heat Exhaust Ventilation | Published by Construction Research Communications Ltd by permission of Building Re- search Establishment Ltd |
| BS 476 | Fire Tests on Building Materials and Structures | |
| Pt 3 | Classification and Method of Test for External Fire Exposure to Roofs | |
| Pt 4
| Non-Combustibility Test for Materials | |
| Pt 5 | Method of Test for Ignitability | |
| Pt 6 | Method of Test for Fire Propagation for Products | |
| Pt 7 | Method of Test to Determine the Classification of the Surface Spread of Flame of Products | |
| Pt 11 | Method for Assessing the Heat Emission from Building Materials | |
| Pt 20 | Method for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Elements of Construction (General Principles) | |
| Pt 21 | Methods for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Load- Bearing Elements of Construction | |
| Pt 22 | Method for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Non-Load- Bearing Elements of Construction | |
| Pt 23 | Methods for Determination of the Contribution of Components to the Fire Resistance of a Structure | |
| Pt 24 | Method for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Ventilation Ducts | |
BS 1230
Pt 1 | Specification for Plasterboard Excluding Materials Submitted to Secondary Operations | Replaced by BS EN 520 |
| BS 2594 | Specification for Carbon Steel Welded Horizontal Cylindrical Storage Tanks | Withdrawn |
| BS 3016 | Specifications for Pressure Regulators for LPG | Replaced by BS EN 16219 |
| BS 4514 | Specification for Unplasticized PVC Soil and Ventilating Pipes of 82.4mm Minimum Mean Outside Diameter, and Fittings and Accessories of 82.4mm and of Other Sizes | |
| BS 5041 | Fire Hydrant Systems Equipment | |
| Pt 1 | Specification for Landing Valves for Wet Risers | |
| Pt 3 | Specification for Inlet Breechings for Dry Riser Inlets | |
| BS 5234 | Partitions (including matching linings) | |
| Pt 2 | Specification for Performance Requirements for Strength and Robustness including Methods of Test | |
| BS 5345 | Selection, Installation and Maintenance of Electrical Apparatus for Use in Potentially Explosive Atmosphere (Other than Mining Applications or Explosive Processing and Manufacturing) | Replaced by BS EN 60079-14 |
| Pt 1 | General Recommendations | |
| Pt 3 | Installation and Maintenance Requirements for Electrical Apparatus with Type of Protection ‘d’. Flameproof Enclosure | |
| BS 5499 | Fire Safety Signs, Notices and Graphic Symbols | |
| Pt 2 | Specification for Self-Luminous Fire Safety Signs | Withdrawn |
| BS 5588 | Fire Precautions in the Design, Construction and Use of Buildings | |
| Pt 5 | CoP for Firefighting Stairways and Lifts | Withdrawn |
| BS 5852 | Methods of Test for Assessment of the Ignitability of Upholstered Seating by Smouldering and Flaming Ignition Source | |
| BS 6206 | Specification for Impact Performance Requirements for Flat Safety Glass and Safety Plastics for Use in Buildings | Replaced by EN 12600 |
| BS 6387 | Test Method for Resistance to Fire of Cables Required to Maintain Circuit Integrity under Fire Conditions | |
| BS 6391 | Specification for Non-Percolating Layflat Delivery Hoses and Hose Assemblies for Fire Fighting Purposes | |
| BS 7346 | Components for Smoke and Heat Control Systems | |
| Pt 2 | Specification for Powered Smoke and Heat Exhaust Ventilators | Withdrawn |
| Pt 3 | Specification for Smoke Curtains | Withdrawn |
| BS 7346 | Components for Smoke and Heat Control Systems | |
| Pt 7 | CoP on Functional Recommendations and Calculation Methods for Smoke and Heat Control Systems for Covered Car Parks | |
| BS 7846 | Electric Cables. Thermosetting Insulated, Armoured, Fire-resistant Cables of Rated Voltage 600/1000V for Fixed Installations, Having Low Emission of Smoke and Corrosive Gases when Affected by Fire. Specification | |
| BS 8202 | Coatings for Fire Protection of Building Elements | |
| Pt 2 | CoP for the Use of Intumescent Coating Systems to Metallic Substrates for Providing Fire Resistance | |
| EN 54 | Fire Detection and Alarm Systems | |
| Pt 2 | Control and Indicating Equipment | |
| Pt 4 | Power Supply Equipment | |
| BS EN 520 | Gypsum Plasterboards. Definitions, Requirements and Test Methods | Replaces BS 1230 Pt 1 |
| BS EN 12101-1 | Smoke & Heat Control Systems – Specification for Smoke Barriers | Replaces BS 7346 Pt 3 |
| BS EN 12101-3 | Smoke & Heat Control Systems – Specification for Powered Smoke & Heat Control Ventilators (Fans) | Replaces BS 7346 Pt 2 |
| BS EN 13501-1 | Fire Test to Building Materials - Classification | |
| BS EN 50054 | Electrical Apparatus for the Detection and Measurement of Combustible Gases. - General Requirements and Test Methods | |
| BS EN 50057 | Electrical Apparatus for the Detection and Measurement of Combustible Gases. - Performance Requirements for Group II Apparatus Indicating up to 100% Lower Explosive Limit | |
| BS EN 50272-2 | Safety Requirements for Secondary Batteries and Battery Installations. Stationary Batteries | Withdrawn |
| BS EN 50272-3 | Safety Requirements for Secondary Batteries and Battery Installations. - Traction Batteries | Withdrawn |
| BS EN 60079-14 | Explosive Atmosphere. Electrical Installations Design, Selection and Erection | Replaces BS 5345 Pt 1 & 3 |
| BS EN IEC 62485-2 | Safety Requirements for Secondary Batteries and Battery Installations - Stationary Batteries | Replaces BS EN 50272-2 |
| BS EN IEC 62485-3 | Safety Requirements for Secondary Batteries and Battery Installations - Traction Batteries | Replaces BS EN 50272-3 |
| EUROPEAN STANDARDS | ||
| EN ISO 1182 | Reaction to Fire Tests for Products – Non-Combustibility Test | |
| EN ISO 1716 | Reaction to Fire Tests for Building Products - Determination of the Gross Heat of Combustion (Calorific Value) | |
| EN ISO 11925 – 2 | Reaction to Fire Tests – Ignitability of Products subjected to Direct Impingement of Flame - Part: Single Flame Source Test | |
| EN ISO 5659 | Plastics – Smoke Generation | |
| Pt 2 | Determination of Optical Density by a Single-chamber Test | |
| EN 3 | Portable Fire Extinguishers | |
| Pt 8 | Additional Requirements to EN 3 – 7 for the Construction, Resistance to Pressure and Mechanical Tests for extinguishers with a Maximum Allowable Pressure Equal to or Lower than 30 Bar | |
| Pt 9 | Additional Requirements to EN 3 – 7 for Pressure Resistance of C02 Extinguishers | |
| EN 54 - 2 | Fire Detection and Alarm Systems - Control and Indicating Equipment | |
| EN 54 - 4 | Fire Detection and Alarm Systems - Power Supply Equipment | |
| EN 81 - 58 | Safety Rules for the Construction and Installation of Lifts. Examination and Tests | |
| Pt 58 | Landing Doors Fire Resistance Test | |
| EN 179 | Building Hardware – Emergency Exit Devices Operated by a Lever Handle or Push Pad | |
| EN 520 | Gypsum Plasterboards – Definitions, Requirements and Test Methods | |
EN 671 - 1 | Fixed Firefighting Systems. Hose Systems. Hose Reels with Semi-Rigid Hose | |
| EN 1125 | Building Hardware – Panic Exit Devices Operated by a Horizontal Bar | |
| EN 1154 | Building Hardware – Controlled Door Closing Devices | |
| EN 1155 | Electrically Powered Hold Open Devices for Swing Doors | |
| EN 1158 | Building Hardware – Door Coordinator Devices – Requirements and Test Standards | |
| EN 1303 | Building Hardware – Cylinders for Locks | |
| EN 1363 | Fire Resistance Tests. General Requirements | |
| EN 1364 | Fire Resistance Test for Non-loadbearing Elements | |
| Pt 1 | Walls | |
| EN 1365 | Fire Resistance Test for Loadbearing Elements. Floors and Roofs | |
| EN 1366 | Fire Resistance Test for Service Installations | |
| Pt 1 | Ventilation Ducts | |
| Pt 3 | Penetration Seals | |
| Pt 4 | Linear Joint Seals | |
| Pt 8 | Smoke Extraction Ducts | |
| Pt 9 | Single Compartment Smoke Extraction Ducts | |
| EN 1634-1 | Fire Resistance and Smoke Control Tests for Door and Shutter Assemblies, Openable Windows and Elements of Building Hardware | |
| Pt 1 | Fire Resistance Test for Door and Shutter Assemblies and Openable Window | |
| EN 1751 | Ventilation for Buildings – Air Terminal Devices – Aerodynamic Testing of Damper and Valves | |
| EN 1906 | Building Hardware. Lever Handles and Knob Furniture. Requirements and Test Method | |
| EN 1935 | Building Hardware. Single-axis Hinges. Requirements and Test Methods | |
| EN 12051 | Building Hardware. Door and Window Bolts. Requirements and Test Methods | |
| EN 12101 | Smoke and Heat Control Systems | |
| Pt 1 | Specification for Smoke Barriers | |
| EN 12209 | Building Hardware. Mechanically Operated Locks and Locking plates. Requirements and Test Methods | |
| EN 12600 | Glass in Building. Pendulum Test. Impact Test Method and Classification for Flat Glass | |
| EN 13501 | Fire Classification of Construction Products and Building Elements | |
| Pt 5 | Classification Using Data from External Fire Exposure to Roofs Tests | |
| EN 13823 | Reaction to Fire Tests for Building Products - Building Products excluding Floorings exposed to the Thermal Attack by a Single Burning Item | |
| EN 14041 | Resilient, Textile and Laminate Floor Coverings. Essential Characteristics | |
| EN 14064 - 1 | Thermal Insulation Products for Buildings. IN-situ Formed Loose-fill Mineral Wool (MW) Products. Specifications for the Loose-fill Products Before Insulation | |
| EN 14064 | Smoke Alarm Devices | |
| EN 14846 | Building Hardware. Locks and Latches. Electromechanically Operated Locks and Striking Plates. Requirements and Test Methods | |
| EN 15684 | Building Hardware – Mechatronic Cylinders – Requirements and Test Methods | |
| EN 16623 | Paints and Varnishes. Reactive Coatings for Fire Protection of Metallic Substrates. Definitions, Requirements, Characteristics and Marking | |
| EN 45545 | Railway Applications – Fire protection on Railway Vehicles | |
| Pt 2 | Determination of Optical Density by a Single-chamber Test | |
| IEC STANDARDS | ||
| IEC 60079 | Explosive Atmospheres | |
| IEC 60331 | Tests for Electric Cables Under Fire Conditions – Circuit Integrity | |
| Pt 25 | Procedures and Requirements – Optical Fibre Cables | |
| IEC 60332 | Tests on Electric and Optical Fibre Cables Under Fire Conditions – All Parts | |
| Pt 1 | Test for Vertical Flame Propagation for a Single Insulated Wire or Cable - Apparatus | |
| Pt 3 | Test for Vertical Flame Spread of Vertically-Mounted Bunched Wires or Cable - Apparatus | |
| IEC 60598-2-22 | Luminaries – Part 2-22: Particular Requirements - Luminaries for Emergency Lighting | |
| IEC 60754 | Test on gases Evolved during Combustion of Materials From Cables | |
| Pt 1 | Determination of the Halogen Acid Gas Content | |
| IEC 61034 | Measurement of Smoke Density of Cables Burning Under Defined Conditions | |
| IEC 61730 | Photovoltaic (PV) Module for Safety Qualification | |
| Pt 2 | Requirements for Testing | |
| ISO STANDARDS | ||
| ISO 834 | Fire resistance Tests - Elements of Building Construction | |
| Pt 1 | General Requirements | |
| Pt 5 | Specific Requirements for Loadbearing Horizontal Separating Elements | |
| Pt 7 | Specific Requirements for Columns | |
| Pt 8 | Specific Requirements for Non-loadbearing Vertical Separating Elements | |
| Pt 9 | Specific Requirements for Non-loadbearing Ceiling Elements | |
| ISO 1896 | Thermal Insulating Asbestos Boards | |
| ISO 3864 | Graphical Symbols – Safety Colours and Safety Signs | |
| Pt 1 | Design Principles for Safety Signs and Safety Markings | |
| Pt 2 | Design Principles for Product Safety Labels | |
| Pt 3 | Design Principles for Graphical Symbols for Use in Safety Signs | |
| ISO 5149 | Refrigerating Systems and Heat Pumps - Safety and Environment Requirements | |
| ISO 5167 | Measurement of Fluid Flow by Means of Differential Pressure Devices | |
| ISO 7010 | Graphical Symbols – Safety Colours and Safety Signs – Registered Safety Signs | |
| ISO 7244 | Air Distribution and Air Diffusion – Aerodynamic Testing of Dampers and Valves | |
| ISO 30061 | Emergency Lighting | |
| FACTORY MUTUAL RESEARCH COPORATION | ||
| FM 1311 | Centrifugal Fire Pumps Spilt-close Type (Axial or Radial) | |
| FM 1319 | Centrifugal Fire Pumps (Horizontal, END Suction Type) | |
Note: - The Standards stated above are non-exhaustive, - SCDF shall not be held responsible for the accuracy of the standard titles shown in Table. | ||
TABLE 1.3A : ABBREVIATIONS
| TABLE 1.3A : ABBREVIATIONS | |
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| ACMV | Air-Conditioning & Mechanical Ventilation |
| AFA | Accessible Floor Area |
| AHJ | Authority Having Jurisdiction |
| ANSI | American National Standards Institute |
| AS | Australian Standard |
| ASHRAE | American Society of Heating, Refrigerating & Air-conditioning Engineers |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| BRE | Building Research Establishment |
| BS | British Standard |
| BSL | Bio-Safety Level |
| CD | Civil Defence |
| CoC | Certificate of Conformity |
| CoP | Code of Practice |
| Cl. | Clause |
| CERT | Company Emergency Response Team |
| DIN | German Institute for Standardization |
| DoC | Declaration of Compliance |
| EC | Exit Capacity |
| EN | European Standard |
| FAMCP | Fully Automated Mechanised Car Park |
| FCC | Fire Command Centre |
| FM | Factory Mutual |
| FMRC | Factory Mutual Research Corporation |
| FSC | Fire Safety Certificate |
| FSE | Fire Safety Engineer |
| HFAD | Home Fire Alarm Device |
| HR | Hour |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| ISO | International Organisation for Standardisation |
| LPG | Liquid Petroleum Gas |
| MAQ | Maximum Allowable Quantity |
| MCST | Management Corporation Strata Title |
| MRA | Mutual Recognition Arrangement |
| MSDS | Material Safety Data Sheet |
| MV | Mechanical Ventilation |
| NFPA | National Fire Protection Association |
| NoA | Notice of Approval |
| NZS | New Zealand Standard |
| ODA | Outdoor Display Area |
| OL | Occupant Load |
| ORA | Outdoor Refreshment Area |
| PE | Professional Engineer |
| PG | Purpose Group |
| PLS | Product Listing Scheme |
| Pt | Part |
| PWDs | Persons With Disabilities |
| QP | Qualified Person |
| RI | Registered Inspector |
| SAC | Singapore Accreditation Council |
| SCDF | Singapore Civil Defence Force |
| SS | Singapore Standard |
| SS EN | Singapore Standard implementation of a European Standard |
| TFP | Temporary Fire Permit |
| UL | Underwriters Laboratories |
| VIFDS | Video Image Fire Detection System |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
TABLE 1.4A : DESIGNATION OF PURPOSE GROUPS
| TABLE 1.4A : DESIGNATION OF PURPOSE GROUPS | |||
| Purpose Group (PG) | Descriptive Title | Purpose for which building or part of the building is used or intended to be used | |
| I | Small residential | Residential dwelling house, such as: | |
| • bungalow • detached house | • semi-detached house • terrace house | ||
| II | Other residential | Accommodation for residential purposes other than any premises comprised in PG I, such as: | |
| • apartment • cluster housing • condominium | • flat • maisonette • town house | ||
| III | Institutional | Establishments used for treatment, care or maintenance of persons suffering from disabilities, such as: | |
| • community hospital • convalescent home • home for intellectually disabled • home for the aged | • home for the spastic • hospice • hospital • psychiatric hospital • nursing home | ||
| Establishments used for care or maintenance of young/ dependent persons, such as: | |||
| • children's home • correction centre • daycare centre • detention centre • dialysis centre | • infant-care centre • rehabilitation centre • school for the spastic • senior activity centre • orphanage | ||
| Establishments used for educational/ training purposes, such as: | |||
| • college • commerical/ private • school • enrichment centre • kindergarten/nursery • military camp | • polytechnic • public school • tuition centre • university • vocational institution | ||
| Establishments used for worker lodging purposes, such as: | |||
| • workers' dormitory | |||
| IV | Office | Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for the purposes of administration and clerical work, or as premises occupied with an office for the purposes of the activities therein carried on, such as: | |
| • banking • insurance • publisher | • stock broker • telephone/ telegraph operating | ||
| V | Shop | Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for the following purposes (and/or any other similar trades or businesses): | |
| • beauty salon • book store • boutique • confectionary outlet • departmental store • drugstore • gift shop • hairdressing salon • jewellery shop • laundry • outpatient clinic • pawnshop | • pet shop/ clinic • polyclinic • provisional shop • shopping arcade • shopping centre • show flat • showrooms for sale of goods • supermarket • take-away F&B • outlet/ kiosk • ticketing agency • travel agency | ||
| VI | Factory | Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors with manufacturing, processing, servicing or testing activities, such as: | |
| • aircraft hangar • chemicals • consumable products • data/ server centre • electrical switching/ transmitting • fireworks • food products • glassware • highly combustible substances • highly flammable products • incineration • metalwork | • oil refinery • pharmaceutical • power generation • recycling • rubber • ship building • telecommunication exchange • vehicle repair/ servicing • wafer • waste treatment/ pumping • woodwork | ||
| VII | Place of public resort | Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for accommodation purpose, such as: | |
| • backpacker hotel • boarding house • hotel • staff quarters | • holiday resort • serviced apartment • student hostel | ||
| Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for educational purpose, such as: | |||
| • auditorium • convention centre • exhibition centre | • museum • public art gallery • public library | ||
| Premises used for social purpose such as: | |||
| • community centre | • private club | ||
| VII | Place of public resort | Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for entertainment purpose, such as: | |
| • casino • cinema • concert hall • discotheque | • internet gaming centre • karaoke lounge • night club • theatre | ||
| Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for religious purpose, such as: | |||
| • church • mosque | • temple | ||
| Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for body treatment purpose, such as: | |||
| • body massage • foot reflexology | • gymnasium • Spa | ||
| Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for recreational purpose, such as: | |||
| • amusement centre • billiard/ snooker centre • bowling centre • roof garden/ terrace • sky garden/ terrace | • public sport complex • public swimming complex • stadium | ||
| Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for F&B purpose, such as: | |||
| • cafeteria • canteen • coffee shop • eating house • fast food outlet | • food court • hawker centre • Pub/ bar • restaurant | ||
| Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for transportation purpose, such as: | |||
| • airport terminal • bus terminal | • ferry terminal • train station | ||
| VIII | Storage | Premises/ areas/ spaces/ floors used for the purposes of storing, depositing or parking of goods, materials and/ or vehicles, such as: | |
| • coldroom • godown • store | • vehicle park • warehouse | ||
| Note: Requirements for buildings not listed in this Table, including but not limited to buildings used for the manufacture and/ or storage of highly combustible substances and/ or flammable liquids, etc., shall be consulted with the SCDF | |||
TABLE 1.4B : OCCUPANT LOAD FACTORS
| TABLE 1.4B : OCCUPANT LOAD FACTORS | ||||
| FUNCTIONAL SPACES | FACTOR (m 2/person) | REMARKS | ||
| Amusement park | 1 | excluding machine areas | ||
| Apartment, residential | 15 | |||
| Area of refuge | ||||
| ambulatory care facility | 1.4 | |||
| custodian care facility | 1.4 | |||
| hospital | 2.8 | |||
| hospital | 0.56 | for area of refuge without patient accommodation | ||
| nursing care facility | 2.8 | |||
| nursing care facility | 0.56 | for area of refuge without patient accommodation | ||
| supervisory care facility | 0.56 | |||
| Archive room | ||||
| reading area | 5 | |||
| stack area | 10 | |||
| Atrium floor | 3 | |||
| Audio visual area | 3 | |||
| Auditorium/ theatre | ||||
| With individual fixed seating | 1.5 | occupant load can be based on number of fixed seating | ||
| With fixed bench seating | --- | occupant load based on 450mm of length of the benches per person | ||
| Audio visual control room for theatres/ cinemas/ concert halls | 5 | |||
| Backpacker hotel | 3 | Max. 20 persons per room (including living area, toilet, etc.) | ||
| Ball room | 1.5 | |||
| Banking hall | 3 | |||
| Bar/ pub | 1 | |||
| Bath room | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Bazaar | 5 | |||
| Billiards room | 5 | |||
| Book/ general storage | 30 | |||
| Bowling alley | 1 | excluding bowling lanes | ||
| Business centre/ office | 10 | |||
| Cafeteria | 1.5 | |||
| Canteen | 1.5 | including staff canteen | ||
| Car parking area | 30 | |||
| Changing room | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Children playground | 5 | including playground equipment | ||
| Classroom | 1.5 | |||
| Computer classroom | 1.5 | |||
| Club room | 1.5 | |||
| Concourse | 3 | |||
| Conference room | 1.5 | |||
| Consultant room | 5 | |||
| Common room | 1.5 | |||
| Computer room | 5 | |||
| Corridor | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Crematoria | 1.5 | |||
| Dance studio | 5 | |||
| Department store | 5 | |||
| Deposit/strong room | 30 | |||
| Design studio | 5 | |||
| Detention room | 3 | |||
| Dining area | ||||
| Hawker centre | 1.5 | |||
| Fast food outlet | 1 | |||
| others | 1.5 | |||
| Discotheque | 1 | including dine & dance area | ||
| Dormitory | 4.2 | bedroom area only, excluding living area, toilet, etc. | ||
| Examination room | 5 | |||
| Exposition/ Trade fair area | 1.5 | |||
| Fast food outlet | 1 | |||
| Filing room/ store | 10 | |||
|
Foyer Bus/ Airport/ Ferry terminal or station |
1.5 | |||
| Fitness club/ centre | 5 | |||
| Function room | 1.5 | |||
| Gallery | ||||
| exhibits | 2.5 | |||
| choir | 1.5 | |||
| prayer | 1.5 | |||
| seating | 1.5 | occupant load can be based on number of fixed seating | ||
| trading | 1.5 | |||
| viewing | 1.5 | |||
| surgical viewing | 3 | |||
| General storage | 30 | |||
| Goods storage | 30 | |||
| Grandstand/ seating area | 1.5 | |||
| Guestroom/ accommodation unit | 15 | min. 2 persons per room or 15m2/person, whichever is higher | ||
| Gymnasium | 3.5 | |||
| Health club/ centre | 5 | |||
| Hobby room | 1.5 | |||
| Housekeeping | 10 | |||
| Indoor games room | 1.5 | |||
| Indoor sport hall | ||||
| school with multi-purpose hall | 3 | |||
| school without multi-purpose hall | 1 | |||
| others | 3 | |||
| Karaoke lounge | 1.5 | including dine & dance areas | ||
| Kitchen/ service area | 10 | |||
| Laboratory | ||||
| healthcare occupancy | 20 | |||
| schools/ colleges/ tertiary institutions | 5 | |||
| others | 5 | |||
| Laundry | ||||
| with machine operation | 15 | |||
| others | 10 | |||
| Lecture room | 1.5 | |||
| Library room | ||||
| stack area | 10 | |||
| reading area | 5 | |||
| Lighting control room | ||||
| theatres/ cinemas/ concert halls | 5 | |||
| others | 5 | |||
| Loading/ unloading area | 4 per bay | |||
| Lobby | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Locker room | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Lounge | 2.5 | |||
| Machine/ printing room | 10 | |||
| Maisonettes, residential | 15 | |||
| Mechanical plant room | 30 | |||
| Meeting room | 1.5 | |||
| Mortuary | 30 | |||
| Multi-purpose hall/ room | ||||
| school/ colleges | 1 | |||
| others | 1.5 | |||
| Multi-purpose sports hall | ||||
| public sport complex | 3 | |||
| public swimming complex | 3 | |||
| stadium | 3 | |||
| others | 3 | |||
| Night club | 1.5 | including dine & dance area | ||
| Nursing station | 10 | |||
| Office | ||||
| Admin/ general | 10 | |||
| director/ manager room | 15 | |||
| drafting room/ area | 5 | |||
| Operation theatre | 7.5 | |||
| Orchestral pit | 1.5 | |||
| Out-patient waiting area | 1.5 | |||
| Packing/ distribution area | 10 | |||
| Pantry | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Passenger arrival/ departure areas | ||||
| Bus/ Airport/ Ferry terminal or station | 1.5 | |||
| Patient accommodation | ||||
| intensive care | 20 | |||
| room | 10 | |||
| ward | 10 | |||
| Pedestrian linkways (aboveground or underground) | ||||
| with commercial activities | 2 | |||
| building to Rapid Transit Stations (e.g., Mass Rapid Transit (MRT)) without commercial activities | 3.5 | |||
| building to building without commercial activities | 5 | |||
| standalone type without commercial activities | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Pharmacy | ||||
| staff area | 10 | |||
| public waiting area | 2 | |||
| Prayer hall | 1.5 | |||
| Pre-function room | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Production area | 10 | automated or non-automated | ||
| Projection room | ||||
| theatres/ cinemas/ concert halls | 5 | |||
| others | 5 | |||
| Promotion area | 1.5 | |||
| Pub | 1 | |||
| Reading room | 5 | |||
| Reception area | 3 | |||
| Recreation room | 1.5 | |||
| Refreshment area | 1.5 | |||
| Restroom | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Restaurant | 1.5 | |||
| Roof | --- | access for maintenance only | ||
| Roof garden/ roof terrace, private | --- | non-simultaneous part of individual residential unit | ||
| Roof garden/ roof terrace, public | ||||
| health/ exercise corner | 5 | with exercise equipment | ||
| jogging track/ designated foot path<=3m in width | 3 | |||
| planter box <300m high | 1.5 | |||
| planter box =>300mm | --- | fully covered with trees/ shrubs | ||
| planter box =>300mm & <= 500mm high | 1.5 | turf | ||
| planter box >500mm high | --- | without step/ ramp access | ||
| sunken/ elevated water feature <300mm in depth/height | 3 | permanent or fixed structure | ||
| sunken/ elevated water feature =>300mm in depth/height | --- | permanent or fixed structure | ||
| sunken planting area | --- | fully covered with trees/ shrubs | ||
| sunken planting area | 1.5 | turf | ||
| other areas | 1.5 | |||
| Seminar room | 1.5 | |||
| Server room | 30 | |||
| Serviced apartment | 15 | per unit | ||
| Service area | 10 | |||
| Shop | 5 | |||
| Showroom | 5 | |||
| Sick room | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Skating rink | ||||
| rink area | 3 | |||
| spectator area | 1.5 | |||
| Snack bar | 1.5 | |||
| Society room | 1.5 | |||
| Spa | 5 | include areas for weight training, aerobics, massage, sauna/steam bath and whirlpools | ||
| Squash court | 2 per court | |||
| Staff office | 10 | |||
| Storage area | 30 | |||
| Staff canteen | 1.5 | |||
| Staff lounge | 3 | |||
| Staff quarters | 15 | min. 2 persons per room or 15m2/person, whichever is higher | ||
| Stage, front/ back | ||||
| schools/ colleges/ tertiary institutions | 3 | |||
| theatres/ cinemas/ concert halls | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Storage/ store room | 30 | |||
| Swimming pool | ||||
| condominium/ apartment | 5 | |||
| hotel | --- | |||
| private club | --- | |||
| public sports complex | 2.5 | |||
| public swimming complex | 2.5 | |||
| serviced apartment | --- | |||
| Swimming pool deck | ||||
| condominium/apartment | 10 | |||
| hotel | 10 | |||
| private club | 10 | |||
| public sports complex | 5 | |||
| public swimming complex | 5 | |||
| serviced apartment | 10 | |||
| Student bedroom | 15 | min. 2 persons per room or 15m2/person, whichever is higher | ||
| Supermarket | 5 | |||
| Therapy centre | 10 | |||
| Ticketing office | 10 | |||
| Toilet | --- | non-simultaneous | ||
| Trading floor | 2 | |||
| Training area | ||||
| public sports complex | 3 | |||
| public swimming complex | 3 | |||
| stadium | 3 | |||
| Treatment room | 5 | |||
| Visitors lounge | 3 | |||
| Waiting area | 3 | |||
| Workshop | ||||
| institutional | 5 | |||
| industrial | 10 | |||
|
Note: - All functional spaces shall be computed based on accessible floor area for the calculation of occupant load, unless specifically exempted under the “Remarks” column - The functional spaces stated above are non-exhaustive. Usage of other occupancy load factor is only allowed if permitted by SCDF |
||||
Updated 3 Mar 2025

