Please enter a keyword to search
9.9.1 Buildings designated for conservation and buildings built before 1969
a. General
Cl.9.9.1 is applicable to buildings with timber floor/ staircase designated for conservation by the authority having jurisdiction or buildings built before 1969. Change of use of these buildings to public accommodation purpose is not permitted. Upgrading of fire safety works shall be applicable to the whole building; partial upgrading of building is not allowed.
b. Timber floor joists and boards without addition of new attic
(1) 2 and 3-storey shophouses
(a) Timber floor boards shall be pressure impregnated with flame retardant chemicals, in order to expose the timber floor joists and boards to retain the existing characteristics of the shophouse. For timber floor joints that fulfil the fire resistance rating requirements, they are not required to be pressure impregnated. Alternatively, timber floor boards shall be lined on the floor joists with non-combustible boards to achieve at least ½-hr fire resistance rating. For residential use, this condition does not apply. Existing timber floors can be retained provided there is no increase in floor areas or addition of a new attic. (See Diagram 9.9.1b.(1)(a) - 1 & 2)
(b) Timber floor joists and boards at the soffit of the five-footway ceiling can be left exposed.
(2) 4-storey shophouses
(a) Timber floor joists and boards shall be lined on the underside between the floor joists with non-combustible boards to achieve at least 1-hr fire resistance rating.
(b) Timber floor joists and boards at the soffit of the five-footway ceiling can be left exposed.
c. Timber floor joists and boards with addition of new attic
(1) 2-storey shophouses
(a) Timber floor boards lined on the underside between the floor joists with non-combustible boards to achieve at least ½-hr fire resistance rating. (See Diagram 9.9.1c.(1)(a))
(b) Timber floor joists and boards at the soffit of the five-footway ceiling can be left exposed.
(c) The floor area of the attic shall not be lower than the highest point of the front façade window at the last storey, i.e. top of the window or fanlight.
(d) The floor area of the attic shall not exceed 50% of the floor immediately below or 50m2, whichever is less, per compartment.
(e) An open connecting staircase to the attic can be considered, provided that the travel distance complies with Cl.9.9.1g..
(2) 3 and 4-storey shophouses
(a) Full protection shall be provided for floor joists and boards of all floors, i.e. timber floor boards shall be lined on the underside between the floor joists to achieve at least 1-hr fire resistance rating. (See Diagram 9.9.1c.(2)(a)).
(b) Timber floor joists and boards at the soffit of the five-footway ceiling can be left exposed.
(c) The floor level of the attic shall not be lower than the highest point of the front façade window at the last storey, i.e., top of the window or fanlight.
(d) The attic floor shall be set-back at least 1.5m from the inner face of the front façade and rear walls to allow for visual connection to the storey below. See Diagram 9.9.1c.(2)(d).
(e) The floor area of the attic shall not exceed 50% of the floor immediately below or 50m2, whichever is less, per compartment.
(f) An open connecting staircase to the attic is allowed provided that the travel distance complies with Cl.9.9.1g..
d. Protection of exit staircases
(1) 2-storey shophouses
(a) Timber staircases, which serve as a means of escape, shall be protected and comply with:
(i) Compartmentation requirements of at least 1-hr fire resistance rating; and
(ii) Pressure impregnation with flame retardant chemicals.
(b) For residential shophouses, without addition of new attic and to be occupied by one family only, the timber staircase can be left exposed and need not be compartmentalised.
(c) For non-residential shophouses, the timber staircase can be left exposed at the second storey level, provided all of the following are complied with:
(i) Travel distances on the second storey are complied with, i.e. the distance from the most remote point of the floor to the edge of the staircase landing is less than 13m or alternative escape staircase is available, e.g. rear escape staircase.
(ii) The timber staircase is compartmentalised at the first storey by at least 1-hr fire-rated enclosures.
(iii) There is no attic level in the second storey.
(2) 3-storey shophouses
(a) Timber staircases, which serve as a means of escape, shall be protected and comply with:
(i) Compartmentation requirements of at least 1-hr fire resistance rating; and
(ii) Pressure impregnation with flame retardant chemicals.
(b) For residential shophouses, without addition of new attic and to be occupied by one family only, the timber staircase can be left exposed and need not be compartmentalised.
(3) 4-storey shophouses
Timber staircases, which serve as a means of escape, shall be protected and comply with:
(a) Compartmentation requirements of at least 1-hr fire resistance rating; and
(b) Pressure impregnation with flame retardant chemicals.
e. Air well and covering over air well
(1) 2-storey shophouses
(a) For air well that has the same usage for all floors, the following coverings shall be used:
(i) A fixed covering up to the level below the main roof eaves with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass, or
(ii) A fully openable covering (retractable or spring open type), by activation of smoke detectors and fire alarm system, up to the level below the roof eaves with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass.
(b) For air well that has different usage for all floors, the following coverings shall be used:
(i) A fixed covering up to the 2nd storey floor level with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass, or
(ii) A fully openable covering (retractable or spring open type), by activation of smoke detectors and fire alarm system, up to the level below the roof eaves with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass.
(c) The air well shall not be enclosed.
(2) 3 and 4-storey shophouses
(a) For air well that has the same usage for all floors, the following coverings shall be used:
(i) A fixed opening up to the third storey level with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass, is allowed, or
(ii) A fully openable covering (retractable or spring open type), by activation of smoke detectors and fire alarm system, up to the level below the roof eaves with, such as non-drip acrylic, non- drip polycarbonate and glass.
(b) For air well that has different usage for all floors, the following coverings shall be used:
(i) A fixed covering up to the 2nd storey floor level with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass, or
(ii) A fully openable covering (retractable or spring open type), by activation of smoke detectors and fire alarm system, up to the level below the roof eaves with approved materials such as non-drip acrylic, non-drip polycarbonate and glass.
(c) The air well shall not be enclosed.
f. Amalgamation of shophouse units
(1) If the amalgamation of shophouses is more than two units, fire shutters or fire doors shall be provided to the openings at the separating wall between every two units of shophouses.
(2) For amalgamation of shophouse units exceeding an AFA of 2000m2, sprinkler system shall be provided for protection against rapid spread of fire due to higher fire load in a larger space.
(3) Timber floor joints and boards shall be provided with full protection for all floors, i.e. covering the underside of the floor boards in between joists with non-combustible boards if the joist size is adequate.
(4) Addition of attic floor shall not exceed 50m2 per compartment.
(5) There shall be at least two independent exit staircases or other exits from every storey of a building, unless otherwise permitted under Cl.9.4.1 and
Cl.9.5.1.
g. Means of escape for all shophouses
(1) If there is only one escape route, the maximum travel distance shall not exceed 13m for non-sprinkler-protected buildings. Residential shophouses not exceeding 3 storeys and occupied by one family only are not subject to this requirement.
(2) Provision of at least ½-hr fire-rated door at the exit staircase discharge can be accepted in lieu of Cl.2.3.3a.(3), which states that there shall be no unprotected openings of occupancy areas within 1.5m horizontally of the internal exit staircase ventilation/discharge point.
h. Alarm system for all shophouses
(1) For shophouses not exceeding 3 storeys and/or amalgamation of not more than 2 shophouse units, manual alarm system is acceptable.
(2) For shophouses exceeding 3 storeys or having an amalgamation of more than 2 units, automatic alarm system shall be provided.
i. Covering of rear courtyard for all shophouses
(1) If there is a protected exit staircase located at the rear courtyard, the entire space can be covered, up to the 2nd storey floor level, provided the exit staircase discharges to the back-lane.
(2) If the exit staircase does not discharge directly to the back-lane but through the rear courtyard, that part of the rear courtyard forming the escape route from the staircase door to the back door shall be made a protected passageway.
j. Direction of door swing for all shophouses
(1) Door swings at the first storey are allowed to swing into the units so as not to obstruct the walkways.
(2) However, where the aggregate occupant load served by the exit staircase exceeds 50 persons, the door shall swing in the escape direction and shall be recessed.
k. Electrical/ water/ gas meters, telecoms trunking and hose reel pipes for all shophouses
(1) For shophouses with a separate exit staircase enclosure at the front leading to the upper storeys, electrical and water meters and Telecoms trunking are allowed to be located within the exit staircase enclosure provided that they are boxed-up with non-combustible materials, e.g. non-combustible boards or metal casing.
(2) All hose reel pipes are to be located within the shophouse and hose reels shall be located near exit doorways.
l. Retention of timber floor in main building to be conserved with new rear extension of reinforced concrete floors
(1) Timber floors in the main building to be conserved with new extension of reinforced concrete floors are subject to the following requirements:
(a) The old and new blocks are to be treated as separate buildings;
(b) Independent escape staircases are to be provided in each of the old and new blocks and the requirement on maximum travel distance is to be complied with;
(c) A fire separation in the form of fire walls and fire doors is to be provided between the old and new blocks (see Diagram 9.9.1l.(1)(c));
(d) Air wells, if provided, shall have a minimum distance of 4m apart between window openings; and
(e) If integration is such that it is considered as a single block, the building (old and new) shall be constructed of reinforced concrete.
(2) Existing timber flooring of PG I residential building under conservation need not comply with the above-mentioned requirements provided that the following conditions are met:
(a) the residential building shall not exceed 3 levels (attic and basement shall be considered as a level);
(b) there shall be no amalgamation of units; and
(c) other requirements stipulated in the conservation requirements, such as protection to the existing timber flooring, etc. shall be complied with.
9.9.2 Temporary buildings on construction sites
All temporary structures/ buildings including site offices or housing quarters on construction sites shall comply with SS 547.
9.9.3 Buildings under construction
For buildings under construction, the following fire safety requirements shall be complied with.
a. Provision of dry & wet risers
(1) All rising mains (dry & wet) shall be made operational for all storeys (except the uppermost 3 storeys) as soon as the uppermost completed storey reaches 24m.
(2) Dry & wet rising mains shall be installed progressively as the building gains height, in order to provide firefighting capabilities during all stages of construction. All outlets, landing valves inlets, water tanks and pumps, where required shall be provided and made readily operational.
b. Provision of normal lift/ passenger hoist
A normal lift shall be provided for the purpose of firefighting. If this is not possible at the construction stage, a passenger hoist (usually installed on site) shall be made available.
c. Provision of electrical supply
A generator set shall be provided for firefighting if the permanent power supply is not available prior to the completion of the building.
d. Provision of fire engine accessway
(1) Adequate fire engine accessway shall be provided where practicable.
(2) Where there is no fire engine accessway provided at site, the quantity of portable fire extinguishers shall be doubled and installed at every floor.
e. Provision of adequate pressure and flow
(1) Rising mains shall be hydraulically tested and a pressure-release valve shall be installed at the highest point of the riser stack. For wet riser system, a break tank of 11.5m3 shall be installed to support firefighting for at least 5 mins. The break tank and fire pumps shall be installed before the building reaches 60m.
(2) For the testing of flow rate for the wet riser system, the topmost landing valve shall be tested (under pump/gravity feed) with a flow rate of at least 27 L/s.
f. Inspection checklist
The inspection checklist attached as Annex 9.9A shall be used for checking fire safety provisions for buildings under construction.
9.9.4 Use of hoardings and safety nets for alteration and alteration work
a. General
The use of hoardings and safety nets in existing buildings undergoing addition and alteration works shall comply with the requirements stated herein.
b. Means of escape
(1) Hoarding erected within building
(a) It shall be constructed of non-combustible material. A minimum of 1.2m wide corridor shall be provided leading to the exit(s). The hoardings shall not obstruct the escape path of occupants within the building.
(b) Alternate means of escape shall be provided outside the hoarded area if the exit(s) is obstructed due to the erection of the hoarding.
(2) Hoardings erected at the external of building
(a) It shall be constructed of non-combustible material and a minimum 1.2m wide foot path shall be maintained for pedestrians. The hoardings shall not obstruct the discharge route of occupants exiting at the 1st storey units and from the exit staircase(s).
(b) It shall not obstruct smoke dispersal and means of escape of nearby buildings. Where the close proximity of the partitions may affect the smoke dispersion and escape of occupants from the nearby building, the partitions shall be located at least 1.2m away from the building.
See Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 1 to 4
c. Fire protection and firefighting provisions
(1) Hoardings erected within building
(a) For addition & alteration works involving sprinkler/ automatic alarm system, the systems covering these areas not under addition & alteration works shall remain active. For areas not involved in addition & alteration works but detector/ sprinkler heads are being isolated due to same zone/ control valve, the management shall arrange for additional surveillance checks so as to be alerted of fire at its incipient stage.
(b) Whenever possible, new systems shall be installed first before deactivating the existing systems so as to minimise the duration of no sprinkler/ automatic alarm protection to the areas affected by A&A works.
(c) The sprinkler/ automatic alarm system shall resume its operation again immediately at the end of the day wherever feasible.
(d) Within the hoarded area(s), 50kg fire extinguisher(s) in trolley shall be provided near the hoarding exit access door. Each fire extinguisher shall not cover more than 20m.
(e) Fire extinguishers and hose reels outside the hoarded area(s) shall be made available.
(2) Hoardings erected at the external of building shall not obstruct public/private hydrant and fire engine accessway/fire engine access road.
d. Fire safety requirements for safety nets
(1) Safety nets shall not obstruct the ventilation opening to rooms/areas where smoke ventilation is required, such as exit staircase, fire lift lobby, smoke-free lobby, flammable stores, kitchen with open-flame cooking, car parks, etc.
(2) No hot work and activities which generate sparks such as welding, cutting and grinding shall be permitted within 3m from the safety net. If unavoidable, these works shall be isolated/ shielded from the safety nets by a non-combustible shielding material.
9.9.5 Engineered timber building construction
a. General
The engineered timber product shall be listed in accordance with the requirements of the product listing scheme.
b. Building design
(1) The habitable height of any healthcare occupancy in an engineered timber building shall not exceed 12m, including mezzanine levels.
(2) A fire safety performance-based (PB) approach shall be adopted in the design of any engineered timber building where its habitable height exceeds 12m.
(3) The engineered timber building shall be fully protected by an automatic sprinkler system.
Exception: An automatic sprinkler system can only be exempted under the following circumstances:
(a) alternative fire protection measures (e.g., fully encapsulated timber elements) are provided to minimise fire damage to the timber structures, in lieu of the sprinkler system;
(b) the building does not exceed 12m in habitable height;
(c) the building is protected by an automatic fire alarm system compliant with SS 645; and
(d) the building does not contain any healthcare occupancy.
(4) Where an automatic sprinkler system is required, the system shall be designed in accordance with SS CP 52. The automatic sprinkler system shall not be shared among different engineered timber buildings if the latter is under different occupier. If the external facade of the engineered timber building is unable to meet the stated performance in accordance with Cl.3.5 for prevention of external fire spread, the external facade shall be required to be protected by a deluge system in accordance to SS CP 52, or any other suppression system that is shown to be effective in preventing vertical fire spread.
(5) The use of engineered timber for elements of structure shall be permitted only for areas above the floor slab of the ground floor. The ground floor slab and basement floors below it shall not have elements of structure constructed using engineered timber.
(6) Essential escape provisions such as staircase shafts and lift shafts of an engineered timber building shall be constructed of non-combustible materials which achieve the necessary fire resistance rating.
Exception: Engineered timber can only be used as elements of structure for essential escape provisions under the following circumstances:
(a) the surfaces of engineered timber elements shall be protected by fire-rated board so that the composite element is able to achieve the necessary fire rating;
(b) the building does not exceed 12m in habitable height; and
(c) the building does not contain any healthcare occupancy.
This exception shall not apply to staircase shelters designed to comply with the Technical Requirements for Storey Shelters.
(7) Essential facilities for fire safety and firefighting operations (such as FCC, fire pump rooms, generator rooms, and smoke-free/ fire lift lobbies) shall be separated from other areas of the engineered timber building project by non-combustible material or encapsulated engineered timber, either of which shall achieve the necessary fire resistance rating.
(8) The use of flammable gas cylinders for cooking is not permitted in the engineered timber building premises if the engineered timber building has access to piped-gas supply for cooking.
(9) Where the usage of the building potentially involves the use of flammable gas cylinders (either for cooking, storage, factory production, etc.) which may result in explosions, the use of engineered timber as elements of structure is not allowed unless the engineered timber building is designed to take into account the explosive actions based on EN 1991 or other relevant internationally recognised standards.
(10) Residential engineered timber building projects shall fully comply with the Technical Requirements for Household Shelters and Technical Requirements for Storey Shelters.
(11) The engineered timber building project shall comply with the design & fire test performance requirements stipulated in European (EN) standards which include BS EN 1995, BS EN 1363, BS EN 1365 & other internationally recognised standards deemed appropriate and necessary by the SCDF.
9.9.6 Use of flammable refrigerants
a. For PG I and II buildings, the use of flammable refrigerants is not permitted in building air-conditioning systems which require installation of piping into occupied areas. This includes both single and multi-split systems.
Exception:
(1) The use of R32 is permitted in split air-conditioning systems.
(2) The use of flammable refrigerants is permitted in refrigerators, and standalone wall-mounted air-conditioners, provided:
(a) the refrigerator or air-conditioner is regulated by the a authority having jurisdiction;
(b) the refrigerator or air-conditioner is meant solely for domestic use;
(c) the amount of flammable refrigerant has a charge weight cap of at most 150g; and
(d) the refrigerant is hermetically sealed within the refrigerator.
b. For PG III to VIII buildings, the use of flammable refrigerants is not permitted in refrigeration systems, e.g., coldrooms, chiller rooms, and food storage factories, which are meant for commercial purposes.
Exception:
The use of flammable refrigerants is permitted in standalone commercial refrigeration systems, provided Cl.9.9.6a.(2)(c) and Cl.9.9.6a.(2)(d) are complied with.
c. For industrial process refrigeration systems, flammable refrigerants are not permitted unless:
(1) there are no alternatives which can achieve the necessary specific performance required for the industrial process; and
(2) workplace safety requirements of the authority having jurisdiction are complied with.
9.9.7 Mega underground developments
a. General
This section provides the broad fire safety requirements for mega underground developments. It is applicable to mega underground developments regardless of size and number of occupants. Mega underground development refers to underground levels with lifts and/ or horizontal access as the primary means of egress. There is no habitable space immediately above the cavern units, which are enclosed chambers within the fire-compartmented underground developments.
b. Means of escape
(1) Each underground development shall be provided with at least two exit shafts.
(2) At least two exit staircases (at least 1.5m in width but not exceeding 2m) located at the exit shafts shall be provided for the underground development. The width of exit staircases shall be determined by the occupant load and uses of the cavern. The minimum width requirement is not applicable to exit staircases serving the cavern units. Such exit staircases shall comply with the requirements stipulated in Cl.2.3.3. Exit staircases are not the primary means of escape.
(3) Fire lift lobby shall be provided at each exit shaft.
(4) All cavern units shall be provided with at least two-way escape regardless of whether one-way travel distance can be complied with. One-way travel distance shall not exceed 20m and two-way travel distance shall not exceed 50m.
(5) The travel distance refers to the distance required to be traversed from the most remote point in the cavern to the edge of a fire door opening directly into the protected corridor.
(6) Protected corridors (enclosed by fire-rated wall/ floor) shall be provided for all cavern units at every storey. The corridor shall have direct access to the protected shaft.
(7) Protected corridors shall be sectorised by fire doors. Each sector shall not consist of more than four cavern units or more than 60m (measure along the corridor). Only those doors in the sectors affected by fire need to be closed during activation of alarm.
c. Structural fire precautions
(1) Fire compartmentation shall be provided for each cavern unit. Each compartment shall not exceed 4000m2 and 15000m3.
(2) Different tenancy units shall be compartmented.
(3) The element of structure/compartment of each cavern unit shall have fire resistance rating of at least 4 hours.
(4) Walls, ceilings, roof covering and finishes containing plastic material shall comply with the requirements stipulated in Cl.3.15.19.
(5) Internal non-load bearing walls and ceilings shall be constructed of non- combustible material.
(6) The surface of a wall or ceiling along protected corridor shall have a surface spread of flame of Class 0 rating.
(7) The exit staircases shall be constructed of masonry. However, if drywall construction is used it shall comply with Cl.3.8.7b..
d. Vehicular access
(1) Fire engine access road having minimum 4m width and overhead clearance of at least 4.5m for access by pump appliance shall be provided for firefighters to conduct firefighting and rescue operations.
(2) Provision to alternative means of vehicle access into the underground development shall be considered.
(3) The fire engine access road shall be protected from fire and smoke, and shall lead directly to the ground level.
(4) Clear smoke height shall be maintained along the access road. Pushing the smoke out directly through the tunnel is not allowed.
(5) Private hydrants shall be provided along the fire engine access road such that every part of the fire engine access road shall be within an unobstructed distance of 50m from the nearest hydrant.
e. Firefighting provisions
A room shall be provided to house the firefighting and rescue equipment. The requirements for storage area are as follows:
(1) two storage areas per storey, with one near each of the exit shafts;
(2) room size shall comply with the dimensions 2m in width, 2m in length and 2.1m in height; and
(3) provision of four 64mm-diameter hoses, four 38mm-diameter hoses, one dividing breeching, two 38mm-diameter nozzles and two complete sets of breathing apparatus.
(4) buggies shall be provided at each level to facilitate firefighting and rescue operations. The requirements for buggies are as follow:
(a) 2 buggies per level. Each near the room storing firefighting equipment;
(b) 4 seaters;
(c) able to mount 1 stretcher;
(d) electrically-operated;
(e) the size of the buggies shall be of approved type by the SCDF; and
(f) the buggies can be used by in-house fire and security personnel provided the buggies are driven back to the holding area during emergency.
f. Firefighting system, detection and alarm
(1) The underground development shall be protected with an automatic sprinkler system.
(2) Wet risers shall be provided such that every part of the underground development is not more than 38m from the nearest wet riser landing valve. The wet riser pipes are allowed to run horizontally but the landing valves shall be located within the protected corridor.
(3) Breeching inlet shall be installed at one of the vertical access shafts at ground level. It shall be located near the FCC.
(4) At least two fire lifts shall be provided for each exit shaft. The fire lift shall have access to every habitable floor and shall be adjacent and accessible to an exit staircase and be approached by a firefighting lobby at each storey. The fire lifts shall home to the ground level (i.e., top of shaft) during activation of alarm and power failure.
(5) All passenger lifts shall be double up as evacuation lift and shall be located within the fire lift lobby. They need not be fire lifts but shall be installed with evacuation switch, connecting to the emergency backup supply, and shall home to ground level in an emergency. The use of these lifts for emergency evacuation shall be supervised by the emergency responders.
(6) The fire lift car shall have a clear area/ space of not less than 2m (depth) x 1.5m (width).
(7) Water mist system can be permitted as substitute of automatic sprinklers provided that the requirements are in accordance with Cl.6.4.6.
(8) FCC shall be located at ground level. It shall be located beside one of the protected shafts.
g. Effective communication systems and holding area
(1) Effective communication system shall be provided for the SCDF at the underground developments to conduct firefighting and rescue operations.
(2) One-way emergency voice communication system such as emergency wireless broadcast system shall be provided for the underground developments. Two-way emergency voice communications system shall be provided between FCC and the essential areas stipulated in Cl.8.2.2.
(3) A holding area shall be provided for the underground development. The size of the holding area shall take into considerations the total occupant load within that floor and shall be calculated based on 0.3m2/person.
(4) The holding area shall be provided with engineered smoke control system and shall have direct connection to the fire lift lobby.
h. Mechanical ventilation and smoke control system
(1) Engineered smoke control system shall be provided for the underground development and fire engine access road.
(2) Exit staircases, smoke-free lobbies and fire lift lobbies shall be pressurised.
(3) The air-handling system for the affected smoke zone and the adjacent zones shall be shut down to avoid re-circulating through the system.
i. Restriction of hazardous materials
(1) Hazardous, flammable and combustible materials shall be prohibited or controlled strictly if they have to be used within the facilities.
(2) If small quantities are needed, special approval has to be obtained from the SCDF.
j. Provision for emergency directional signage/ generator
(1) Photoluminescent marking/ tape to guide occupants along evacuation routes to appropriate exits shall be provided:
(a) along internal walls and/ or floors of the exit staircase and protected lobby;
(b) at the exit staircase door; and
(c) in designated corridor with exit directional sign.
(2) The duration of operation for standby generator shall be in accordance with the requirements stipulated in SS 535.
(3) Lifts at the cavern units shall be connected to the standby generator.
Diagram 9.9.1b.(1)(a) - 1 : Retaining existing 2-storey shophouse
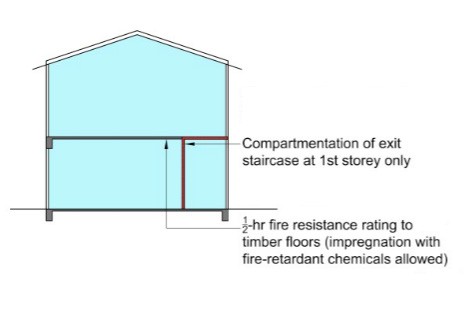
Diagram 9.9.1b.(1)(a) - 1 : Retaining existing 2-storey shophouse
Diagram 9.9.1b.(1)(a) - 2 : Retaining existing 3-storey shophouse
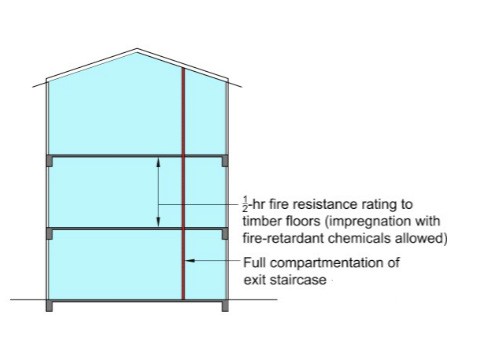
Diagram 9.9.1b.(1)(a) - 2 : Retaining existing 3-storey shophouse
Diagram 9.9.1c.(1)(a) : Adding new attic to existing 2-storey shophouse
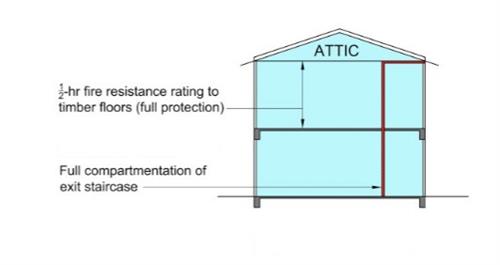
Diagram 9.9.1c.(1)(a) : Adding new attic to existing 2-storey shophouse
Diagram 9.9.1c.(2)(a) : Adding new attic to existing 3-storey shophouse
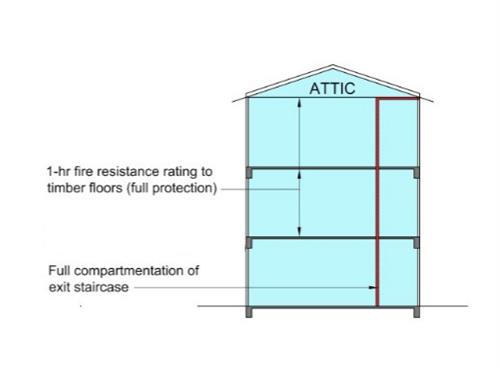
Diagram 9.9.1c.(2)(a) : Adding new attic to existing 3-storey shophouse
Diagram 9.9.1c.(2)(d) : Visual connection between the attic and the floor below
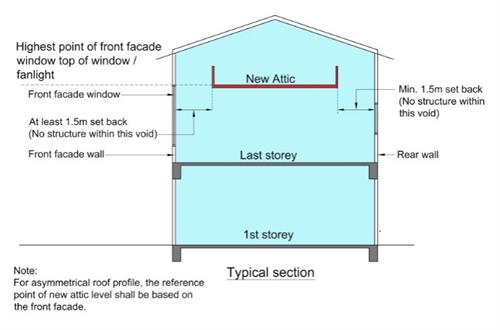
Diagram 9.9.1c.(2)(d) : Visual connection between the attic and the floor below
Diagram 9.9.1l.(1)(c) : Fire separation between the old and new blocks
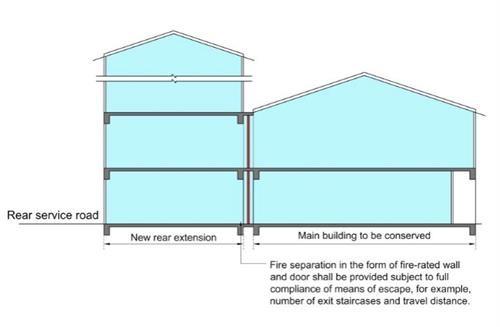
Diagram 9.9.1l.(1)(c) : Fire separation between the old and new blocks
Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 1 & 2 : Hoarding obstructing means of escape

Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 1 : Hoarding obstructing means of escape
-2.png?sfvrsn=c09994c1_1)
Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 2 : Hoarding obstructing means of escape
Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 3 & 4 : Hoarding obstructing openings for smoke dispersal

Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 3 : Hoarding obstructing openings for smoke dispersal

Diagram 9.9.4b.(2) - 4 : Hoarding obstructing openings for smoke dispersal
Updated 3 Sep 2025

